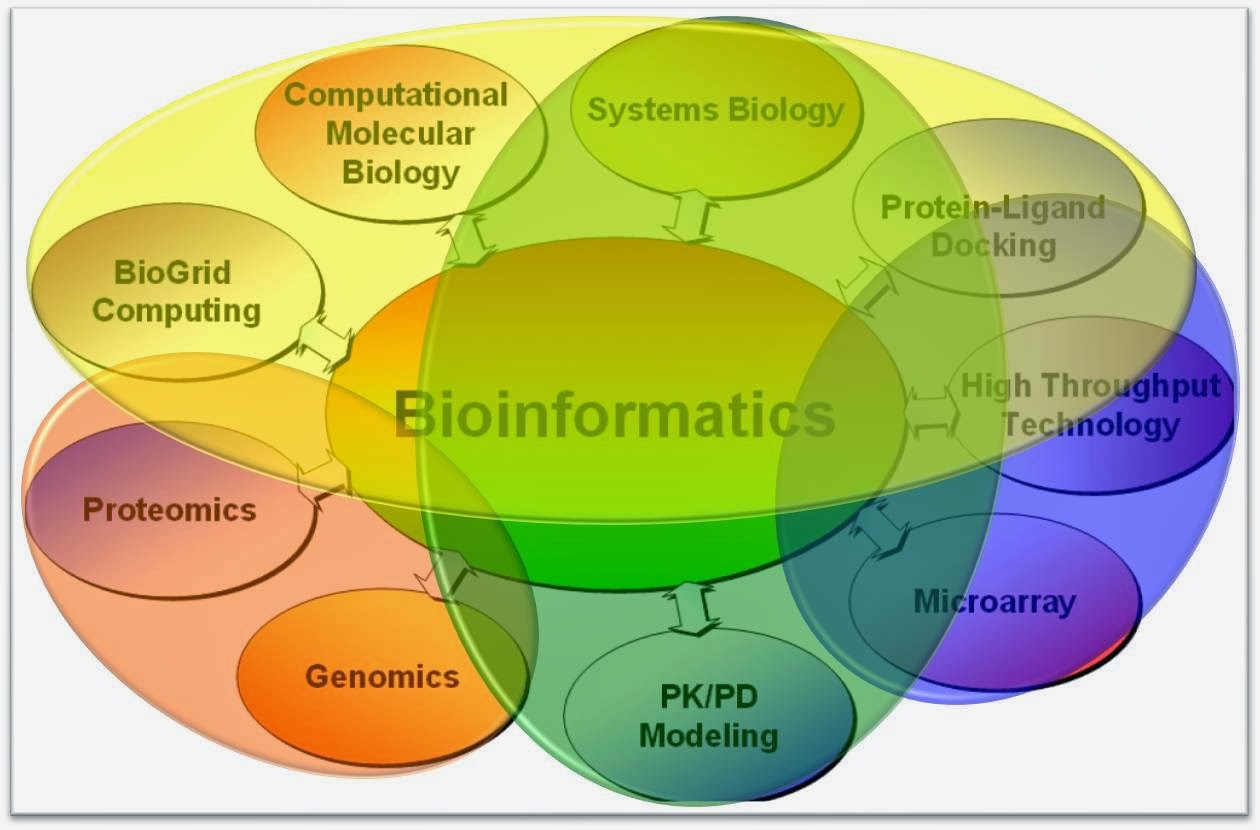
What is bioinformatics? Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field of computer technology to the management of biological information that develops and improves on methods for analyzing, storing, and retrieving biological data. It has been started since 1968. In the past three decades, bioinformatics had seen extraordinary development and use in many areas of computer science, mathematics, engineering, and life sciences to process biological data. However, the term bioinformatics is recently invention, and not appearing in the literature until early 1990s. It’s also known as bioinformatics computational biology.
Bioinformatics plays a few important roles such as in the textual mining of the development of biological and gene ontologies; and in analysis of gene and protein structures. However, bioinformatics favor of the development of algorithms, theory and statistical techniques and calculations to solve the problem stems from the need to manage and analyze biological data. Bioinformatics tools aid in the comparison of genetic and genomic data. The comparison of the genes in the same species or between different species can show similarities of protein functions, or relations between the phylogenetic species.
The goal of bioinformatics is to determine the sequence of the entire human genome. Bioinformatics is a powerful new technology for the efficient management, analysis, and search of bio-medical data. The main concern of the bioinformatics is the use of mathematical tools to extract useful information from the chaotic data was collected using data mining technology.
Bioinformatics now entails the creation and advancement
of databases, algorithms, computational and statistical techniques, and theory
to solve formal and practical problems arising from the management and analysis
of biological data
-sm.jpg)